Exploring Diamond Anatomy: The Number of Sides on a Diamond
Diamonds are often celebrated for their brilliance and beauty, but their allure goes beyond surface-level aesthetics. Understanding the anatomy of a diamond, particularly its facets and cuts, is essential for anyone looking to appreciate these precious gems or invest in diamond jewelry. This article delves into the basics of diamond shapes and cuts, the anatomy of a diamond, the significance of facets, and the factors that influence a diamond's overall quality.
The Basics of Diamond Shapes and Cuts
Diamonds come in various shapes and cuts, each influencing how light interacts with the stone and, consequently, its sparkle and visual appeal. The term "cut" refers not just to the shape (like round or princess) but also to how well the diamond has been crafted. The quality of the cut can significantly affect the diamond's brilliance and fire, the terms used to describe the sparkle and colorful flashes of light that diamonds emit.
Common Diamond Shapes:
- Round: The most popular shape, known for its optimal light reflection.
- Princess: A square shape with pointed corners, ideal for modern styles.
- Emerald: Characterized by a rectangular shape with step cuts that highlight clarity.
- Asscher: Similar to emerald cuts but square in shape, offering vintage charm.
- Oval, Pear, and Marquise: These shapes provide a unique look while maximizing carat weight.
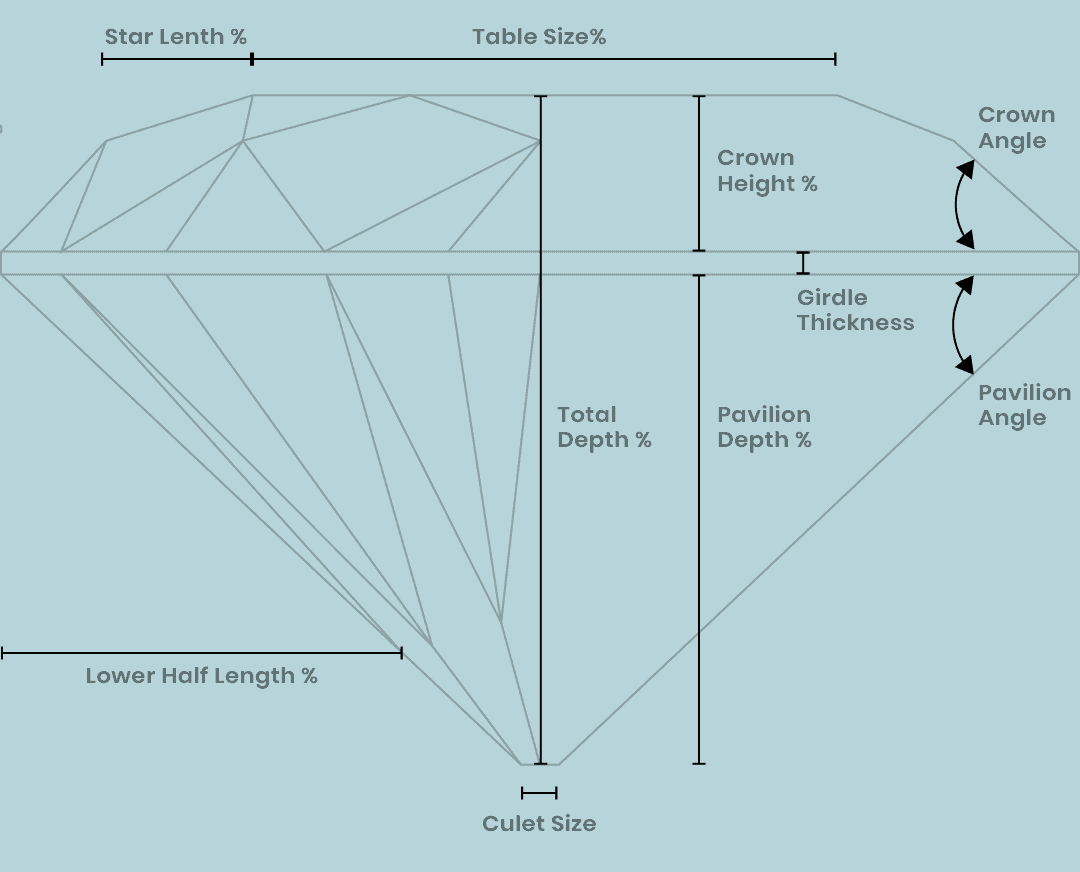
The Anatomy of a Diamond
A diamond's anatomy can be broken down into several parts, including the crown, table, girdle, pavilion, and culet. Each section contributes to the diamond's overall appearance and performance.
- Crown: The upper portion of the diamond above the girdle, responsible for reflecting light.
- Table: The flat top surface of the diamond, which plays a crucial role in light entry.
- Girdle: The narrow band that separates the crown from the pavilion; it serves as a reference point for the diamond's size.
- Pavilion: The lower portion of the diamond, which helps to reflect light back through the crown.
- Culet: The very bottom point of the diamond; while traditionally flat, it can be pointed or cut to various shapes.
Diamond Facets and Sides
Facets are the flat surfaces that make up the diamond's shape and design. The arrangement and number of facets play a pivotal role in how light interacts with the stone, creating its brilliance and fire.
The Importance of Facets:
- Light Reflection: Well-placed facets allow for maximum light reflection, enhancing the diamond's sparkle.
- Visual Appeal: The arrangement of facets contributes to the diamond's aesthetic appeal, influencing how the stone appears to the naked eye.
- Cut Quality: The precision in cutting and polishing facets directly impacts the diamond's overall quality and value.
The Round Brilliant Cut
The round brilliant cut is the most popular diamond cut, renowned for its exceptional ability to reflect light. It typically consists of 58 facets, including the crown, pavilion, and table. The arrangement of these facets is specifically designed to maximize the diamond's brilliance, making it a favorite choice for engagement rings and other fine jewelry.
Characteristics of the Round Brilliant Cut:
- Facets: 58 (33 in the crown and 25 in the pavilion)
- Proportions: Ideal proportions enhance light performance, maximizing sparkle.
- Versatility: Complements various settings and styles, appealing to a wide range of tastes.
Fancy Cut Diamonds
Fancy cut diamonds encompass all shapes other than the classic round brilliant cut. This category includes diamonds like the princess, oval, marquise, and heart shapes. While they may not always offer the same level of brilliance as round diamonds, fancy cuts have their unique charm and can often appear larger than their carat weight due to their elongated shapes.
Popular Fancy Cuts:
- Princess Cut: A modern cut known for its sharp corners and brilliance.
- Cushion Cut: A vintage-inspired shape with rounded corners, often referred to as "pillow" cut.
- Heart Cut: A romantic shape symbolizing love, typically used in pendants and earrings.
Evaluating Diamond Cut Quality
When assessing a diamond's quality, the cut is one of the most critical factors to consider. Cut quality is determined by the diamond's proportions, symmetry, and polish, which collectively influence how well the diamond interacts with light.
Key Factors in Cut Quality:
- Proportions: The dimensions of the crown and pavilion, including angles and depth.
- Symmetry: The uniformity of the diamond's facets and their alignment.
- Polish: The smoothness of the diamond's surface, which affects light performance.
A well-cut diamond will exhibit a balance of brilliance, fire, and scintillation, making it visually striking and desirable.
Diamond Proportions and Symmetry
The proportions of a diamond refer to the specific measurements of its various parts, while symmetry relates to the arrangement of its facets. Both aspects are crucial in determining a diamond's visual appeal and performance.
Importance of Proportions:
- Brilliance: Well-balanced proportions allow light to enter and exit the diamond effectively, enhancing its brilliance.
- Durability: Correct proportions contribute to the diamond's structural integrity, minimizing the risk of chipping or breaking.
Evaluating Symmetry:
A symmetrical diamond will have evenly shaped and aligned facets, contributing to a pleasing overall appearance. In contrast, asymmetrical diamonds may exhibit uneven light performance and a less desirable look.
Diamond Clarity and Inclusions
Diamond clarity refers to the presence of internal or external flaws, known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively. These imperfections can affect the diamond's value and appearance.
Clarity Grades:
- Flawless (IF): No inclusions visible under 10x magnification.
- VVS1/VVS2: Very, very slight inclusions difficult to detect.
- VS1/VS2: Very slight inclusions visible under magnification but difficult to see with the naked eye.
- SI1/SI2: Slight inclusions visible with the naked eye but do not significantly impact beauty.
- I1/I2/I3: Inclusions visible to the naked eye, potentially affecting brilliance.
Higher clarity grades generally command higher prices, but many diamonds with lower clarity still exhibit beauty and brilliance.
Buying Diamond Jewelry
When purchasing diamond jewelry, it's essential to consider factors such as cut, shape, clarity, and budget. Here are some tips to help you make informed decisions:
- Educate Yourself: Familiarize yourself with the 4 Cs - cut, color, clarity, and carat weight - to understand the factors influencing diamond quality and value.
- Set a Budget: Determine your spending limit to narrow down your options and avoid overspending.
- Choose a Reputable Jeweler: Purchase from established jewelers who provide certification and information about the diamonds they sell.
- Consider Personal Style: Think about the recipient's taste and style when selecting diamond jewelry, ensuring it complements their preferences.
In Conclusion
Understanding the anatomy of a diamond, from its facets and cuts to its clarity and proportions, is essential for anyone looking to appreciate or purchase these remarkable gemstones. Whether opting for a classic round brilliant or a unique fancy cut, knowing what to look for can help you select a diamond that not only shines but also holds lasting value. Investing time in understanding diamond anatomy can lead to a more fulfilling and confident purchasing experience, allowing you to choose a piece of jewelry that will be cherished for years to come.
FAQs: Exploring Diamond Anatomy
What is diamond anatomy?
How many sides does a standard diamond have?
What are facets, and why are they important?
What is the significance of the crown and pavilion?
How does the cut of a diamond affect its beauty?
What are the common diamond shapes and their facet counts?
- Round Brilliant: 58 facets
- Princess Cut: 76 facets (average)
- Emerald Cut: 50 facets
- Asscher Cut: 58 facets
- Cushion Cut: 58 facets
- Marquise Cut: 56 facets
- Oval Cut: 56 facets
- Pear Cut: 58 facets
What role does symmetry play in diamond quality?
How can I evaluate diamond clarity?
What is the difference between a round brilliant cut and fancy cut diamonds?
How should I choose a diamond based on its anatomy?
























